Cultured to propagate
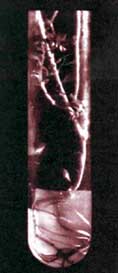 PLANTS can be cultivated in test-tubes that contain the appropriate nutrient medium. Any part of the plant can be inoculated into the medium to produce a large number of plants. This system is far more efficient and cost-effective as compared to conventional methods of multiplication.
PLANTS can be cultivated in test-tubes that contain the appropriate nutrient medium. Any part of the plant can be inoculated into the medium to produce a large number of plants. This system is far more efficient and cost-effective as compared to conventional methods of multiplication.
Tissue culture, to begin with, is a good method for understanding the factors responsible for cell differentiation and organ formation. An important application of plant tissue culture is micropropagation of endangered species - over a million plants can be produced from a microscopic segment of plant tissue within 12 months. Such a prolific rate of multiplication cannot be expected of any other method. Production of disease-free plants by the eradication of virus has been an outstanding contribution of tissuk culture technology towards horticulture and cultivation of forest crops. In addition, a large number of genetic manipulations can be done using this technique.
The potential use of plant tissue culture for the production of compounds valuable to the industry has long been a subject of interest for 'biotechnologists as well. Higher plants are valuable sources of industrially important natural products which include flavors, fragrances, essential oils, pigments, sweeteners, feedstocks, antimicrobials and pharmaceuticals. In most instances, these chemical compounds belong to a group@ collectively referred to as secondary metabolites. Plant cell cultures have advantages in production of these metabolites over intact (non -experimental) plants due to the fact that the rate of cell growth and biosynthesis in cultures initiated from a very small amount of plant material is quite high. As a result, the final product may be produced in a considerably short period of time. This is in contrast to large amount of mature plant tissues processed to obtain a small quantity of drug.
The natural sources for the manufacture of these products are not enough to meet consumers' demand and therefore, efforts have to be made to develop this tissue culture technology for their production at an industrial level.
Related Content
- New study uncovers the underlying causes of Delhi’s air pollution problems
- Development of high-yield influenza A virus vaccine viruses
- Slip pulse and resonance of Kathmandu basin during the 2015 Mw 7.8 Gorkha earthquake, Nepal imaged with geodesy
- Time for people to come forward, save Ganga'
- Bamboo tissue culture helping Tripura cultivators to boost production
- Need for creation of lichen gardens and sanctuaries in India
