The price of power
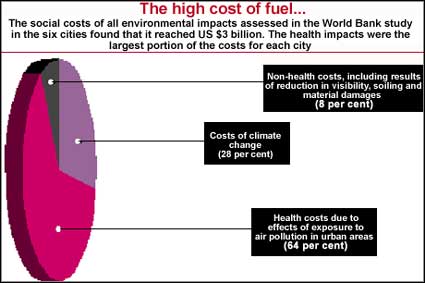 A significant source of urban air pollution is the combustion of fuels by power plants, industrial boilers, residential stoves and vehicles. A World Bank study in 1998 assessed the magnitude of various damages from this. This method of analysis was applied to six large cities in different countries: Bangkok, Thailand; Krakow, Poland; Manila, the Philippines; Mumbai, India; Santiago, Chile; and Shanghai, China. Cost of damage to health was the highest, in which premature death accounted for 40 per cent. The evidence is likely to represent the state of the environment in many urban areas of developing countries.
A significant source of urban air pollution is the combustion of fuels by power plants, industrial boilers, residential stoves and vehicles. A World Bank study in 1998 assessed the magnitude of various damages from this. This method of analysis was applied to six large cities in different countries: Bangkok, Thailand; Krakow, Poland; Manila, the Philippines; Mumbai, India; Santiago, Chile; and Shanghai, China. Cost of damage to health was the highest, in which premature death accounted for 40 per cent. The evidence is likely to represent the state of the environment in many urban areas of developing countries.
Related Content
- Managing the seasonal variability of electricity demand and supply
- Net zero energy by 2060: charting the path of Europe and Central Asia toward a secure and sustainable energy future
- Towards a rooftop solar transition in Bangladesh
- Procedure for implementation of uniform renewable energy tariff
- Renewable power generation costs in 2022
- Key indicators for Asia and the Pacific 2023
