Health of developing nations
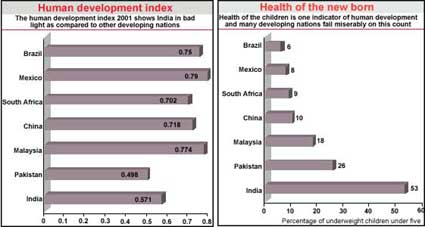 Developing nations prioritise expenditure and social costs, like that for pubic health, are the first to be axed. The Human Development Report 2001 indexes the overall development by including the expenditure made on health related activities. Developing countries, specially India, come out culprits for ignoring the health of its citizens. On the other hand, the exhorbitant costs of medication, as in the case of AIDS treatment make life harder for people suffering in these countries. While governments need to commit more to health needs, an adequate regime for cheap drugs is also the need of the hour.
Developing nations prioritise expenditure and social costs, like that for pubic health, are the first to be axed. The Human Development Report 2001 indexes the overall development by including the expenditure made on health related activities. Developing countries, specially India, come out culprits for ignoring the health of its citizens. On the other hand, the exhorbitant costs of medication, as in the case of AIDS treatment make life harder for people suffering in these countries. While governments need to commit more to health needs, an adequate regime for cheap drugs is also the need of the hour.
| Cost of cure | ||||
| High costs of medication and cures prevent a healthy global population. The case of AIDS treatment is symptomatic | ||||
| Switzerland | Kenya | Zambia | Uganda | |
| Population | 7 million | 30 million | 10 million | 23 million |
| People with HIV | 17,000 | 2,100,000 | 870,000 | 820,000 |
| Cost of treating all infected people with antiretroviral drugs at global market prices, at about $12,000 a person a year (in US $) | 204 million | 25 billion | 10 billion | 10 billion |
| Cost of treatment as per cent of GDP | 0.08 | 238 | 154 | 336 |
Related Content
- Reply by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) regarding use of environmental compensation funds, 29/04/2025
- Advancing sustainable development in Africa
- Report by Court Commissioner on Ghazipur landfill and waste to energy plant at the landfill, 29/03/2025
- Order of the National Green Tribunal regarding mismanagement of waste by Nagar Parishad Danapur Nizamat, Patna, Bihar, 27/03/2025
- Order of the National Green Tribunal regarding garbage dumping in Danapur, Patna, Bihar, 27/03/2025
- Central Pollution Control Board report on plastic waste management rules and microplastics, 26/03/2025
