A dot for a nucleotide
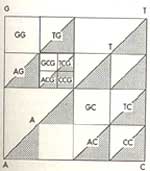 IN GENOME Mapping, the entire DNA sequence is mapped in a square whose corners and the associated quadrants are marked A, T, G, C, to represent the four nucleotides that comprise DNA. A nucleotide is represented by a dot in the appropriate quarter or quadrant of the square on the computer screen. Its position within the quadrant is dependent on the previous nucleotide in the sequence.
IN GENOME Mapping, the entire DNA sequence is mapped in a square whose corners and the associated quadrants are marked A, T, G, C, to represent the four nucleotides that comprise DNA. A nucleotide is represented by a dot in the appropriate quarter or quadrant of the square on the computer screen. Its position within the quadrant is dependent on the previous nucleotide in the sequence.
The point at which the plotting is begun is the centre of the square. The first nucleotide is plotted halfway between the origin and the corner corresponding to the nucleotide, the second nucleotide is plotted midway between the first point and the corner corresponding to the second nucleotide, and so on.
Each quadrant denotes sub-sequences ending with the nucleotide marked at the corner of the quadrant. Each of the four quadrants are further divided into four sub-quadrants, each describing sequences whose last two nucleotides are identical.
Related Content
- Genome-wide excision repair in Arabidopsis is coupled to transcription and reflects circadian gene expression patterns
- Novel plasmid-mediated colistin resistance gene mcr-3 in escherichia coli
- Identification of a novel plasmid-mediated Colistin-resistance gene, mcr-2, Inescherichia coli, Belgium, June 2016
- Whole genome sequencing for genomics-guided investigations of Escherichia coli O157:H7 outbreaks
- Association of p53 codon72 Arg> Pro polymorphism with susceptibility to nasopharyngeal carcinoma: evidence from a case–control study and meta-analysis
- An integrated map of structural variation in 2,504 human genomes
