Transforming India’s approach to cancer care
In India, a country with a vast population and a diverse socio-economic fabric, healthcare remains fraught with challenges including disparities in access. These socio-economic disparities are deep, and
In India, a country with a vast population and a diverse socio-economic fabric, healthcare remains fraught with challenges including disparities in access. These socio-economic disparities are deep, and
In 1999, a scientist at the Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory in the US faked crucial evidence linking power lines to cancer in the <i>Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences </i> and <i>F E B S Letters</i>. <br><br> In 2002, claims by researchers at Bell Labs in the US on creation of molecular-scale transistors were proved wrong. Journals <i>Science</i> <i>Nature</i> published the papers. <br>
india has reported two new advances in cancer diagnostics and treatment. The reports were among the top three presented at the
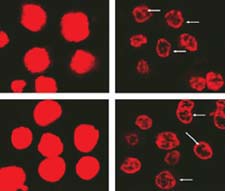
venom spewed by the deadly Indian black scorpion (Heterometrus bengalensis) could have a possible cure for human blood cancer, a new research claims. A joint team from Indian Institute of Chemical
This report has two overall general purposes. The first is to summarise, assess, and judge the most comprehensive body of evidence yet collected and displayed on the subject of food, nutrition, physical activity, body composition, and the risk of cancer, throughout the life-course.

us scientists have produced a device that could potentially screen patients for lung cancer. The new device works from a known principal
in february, the us state of New Mexico rejected two bills demanding a ban on the use of aspartame, an artificial sweetener in food items. Aspartame, found in products like cough syrups, chewing
<p>Benzene exposure from vehicular sources and its health impact are relatively unexplored in India. We have investigated in this study hematology and lymphocyte subsets of 25 petrol pump attendants, 25 automobile service station workers and 35 controls matched for age, sex and socioeconomic conditions.

people with a specific variation in a gene who are exposed to arsenic have greater risk of getting skin lesions and hyperkeratosis, a precursor to skin cancer, say researchers from Kolkata. The gene,

using bio-fuel for cooking could lead to cardiovascular diseases and cancer, says a research team from Chittaranjan National Cancer Institute, Kolkata. The team found that biomass smoke causes the
researchers have found an increased risk of bladder cancer due to exposure to chlorinated water through drinking, swimming and bathing. The study was published online in the January 15, 2006, issue